The Solar Geoengineering Updates Newsletter (October'2024)
Welcome to the Solar Geoengineering Updates Newsletter, a monthly newsletter that updates you on the developments of everything SRM-related.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Deadlines
2. Research Papers
3. Web Posts
4. Reports
5. Job Opportunities
6. Upcoming Events
7. Podcasts
8. YouTube Videos
Note: Click on the headings listed in the table of contents above to easily navigate to the sections you're interested in.
DEADLINES
NOAA request for comments on potential solar radiation modification research regulation | Deadline 19 November 2024
(NEW) Call for Proposals for 2025 Degrees Global Forum Conference | 08 December 2024
Call for Proposals—Exploring Climate Cooling | Deadline: 09 December 2024
Submit your recent research on Solar Radiation Management to new ES: Atmospheres collection | Deadline: 31 January 2025
Call for Proposals-Solar Radiation Management | Deadline to apply: 27 February 2025
RESEARCH PAPERS
Microphysical Interactions Determine the Effectiveness of Solar Radiation Modification via Stratospheric Solid Particle Injection
Vattioni, S., Käslin, S. K., Dykema, J. A., Beiping, L., Sukhodolov, T., Sedlacek, J., ... & Chiodo, G. (2024). Microphysical interactions determine the effectiveness of solar radiation modification via stratospheric solid particle injection. Geophysical Research Letters, 51(19), e2024GL110575.
Synopsis: In this study, scientists report that shooting 5 million tons of diamond dust into the stratosphere each year could cool the planet by 1.6ºC—enough to stave off the worst consequences of global warming. Moreover, the 3D climate model showed diamond dust could reflect sunlight, remain airborne for a long time and avoid clumping, all while being chemically inert—meaning no acid rain formation. But. the scheme wouldn’t be cheap, however: experts estimate it would cost nearly $200 trillion over the remainder of this century—far more than traditional proposals to use sulfur particles.
Demographics shape public preferences for carbon dioxide removal and solar geoengineering interventions across 30 countries
Sovacool, B. K., Evensen, D., Baum, C. M., Fritz, L., & Low, S. (2024). Demographics shape public preferences for carbon dioxide removal and solar geoengineering interventions across 30 countries. Communications Earth & Environment, 5(1), 642.
Synopsis: Climate intervention survey across 30 countries reveals key demographic divides in preferences for solar geoengineering. Support is generally higher among younger populations and those in poverty, especially in the Global South. Gender has minimal influence, but age, income, and region significantly shape attitudes toward these interventions.
Global perspectives on solar geoengineering: A novel framework for analyzing research in pursuit of effective, inclusive, and just governance
Dove, Z., Hernandez, A., Talati, S., & Jinnah, S. (2024). Global perspectives on solar geoengineering: A novel framework for analyzing research in pursuit of effective, inclusive, and just governance. Energy Research & Social Science, 118, 103779.
Synopsis: A new framework examining research on solar geoengineering (SG) perceptions reveals notable biases: studies largely focus on perspectives from the Global North, underrepresent youth voices, and often aim to increase public support for SG, sidelining other lines of inquiry. Cross-cultural insights, especially on public engagement and capacity building, are frequently overlooked. To address these gaps, recommendations call for more inclusive, justice-centered approaches to enhance SG governance and representation in future studies.
The Development of a Floating Mono-Particle “Sun Shield” to Protect Corals from High Irradiance during Bleaching Conditions
Scofield, J. M., Prime, E. L., Flores, F., Severati, A., Mongin, M., Bougeot, E., ... & Qiao, G. G. (2024). The Development of a Floating Mono-Particle “Sun Shield” to Protect Corals from High Irradiance during Bleaching Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(10), 1809.
Synopsis: Coral bleaching is intensifying due to climate change. This study introduced a new “sun shield” technology, using a monolayer of reflective calcium carbonate particles that reduces sunlight by ~20% over coral reefs. Modeling shows this shield could lower bleaching stress across 1.5 km² by cutting reactive oxygen buildup. With further refinement, this method could protect vulnerable reefs during heatwaves, reducing bleaching impact on a small scale.
New submodel for emissions from Explosive Volcanic ERuptions (EVER v1.1) within the Modular Earth Submodel System (MESSy, version 2.55.1)
Kohl, M., Brühl, C., Schallock, J., Tost, H., Jöckel, P., Jost, A., ... & Pozzer, A. (2024). New submodel for emissions from Explosive Volcanic ERuptions (EVER v1. 1) within the Modular Earth Submodel System (MESSy, version 2.55. 1). EGUsphere, 2024, 1-35.
Synopsis: A methodological study introduces EVER v1.1, a submodel for tracer emissions from explosive volcanic eruptions, developed within the Modular Earth Submodel System (MESSy). EVER quantifies gaseous and aerosol tracers based on eruption parameters and facilitates mapping of volcanic ash sizes. Evaluated using the ECHAM/MESSy Atmospheric Model (EMAC) alongside satellite data from the 2011 Nabro eruption, it highlights sensitivities in emission parameters. The study proposes a standardized setup for simulating volcanic impacts on stratospheric SO₂ from 1990 to 2023, with potential applications in volcanic ash, wildfires, and solar geoengineering research.
A new method for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions in climate models
Duran, B. M., Wall, C. J., Lutsko, N. J., Michibata, T., Ma, P. L., Qin, Y., ... & Debolskiy, M. (2024). A new method for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions in climate models. EGUsphere, 2024, 1-41.
Synopsis: This study introduces a method for estimating shortwave effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions (ERFaci) using histograms of cloud fraction, droplet effective radius, and liquid water path. Applied to five CMIP6 models, the method yields total SW ERFaci estimates that align with established techniques. Findings indicate that since 1850, the Twomey effect contributed −0.34 Wm−2, liquid water path adjustments contributed −0.22 Wm−2, and cloud fraction adjustments contributed −0.09 Wm−2. This approach enhances the accuracy of diagnosing ERFaci components, crucial for reducing uncertainty in historical climate forcing estimates.
Change in Wind Renewable Energy Potential Under Stratospheric Aerosol Injections
Baur, S., Sanderson, B. M., Séférian, R., & Terray, L. (2024). Change in Wind Renewable Energy Potential under Stratospheric Aerosol Injections.
Synopsis: This study investigates the impact of Stratospheric Aerosol Injections (SAI) on wind renewable energy (WRE) potential under different emission scenarios. Using the CNRM-ESM2-1 Earth System Model, results indicate that while global WRE potential remains largely unchanged under SAI compared to SSP scenarios, regional variations are significant, with fluctuations reaching ±12% in WRE potential. Notably, SAI modifies large-scale circulation patterns, leading to a pronounced poleward jet shift in the Southern Hemisphere. This research underscores the complex interactions between SRM strategies and wind patterns, informing future mitigation efforts.
Political ideology and views toward solar geoengineering in the United States
Magistro, B., Debnath, R., Ebanks, D., Wennberg, P., & Alvarez, R. M. (2024). Political ideology and views toward solar geoengineering in the United States.
Synopsis: This study explores how familiarity with solar geoengineering (SG) affects political polarization regarding climate change among American voters. Analyzing a nationally representative sample of 2,109 individuals, the findings reveal that greater familiarity with SG correlates with diminished political divides, particularly in support for SG, concerns about its risks, and preferred climate strategies. This suggests that increasing awareness of SG could facilitate bipartisan engagement on climate policy, offering a pathway to overcome ideological barriers in climate action.
Impacts of Solar Geoengineering on Malaria Transmission in South Asia [Preprint]
Hussain, A., Khan, M. A., & Shoaib, M. (2024). Impacts of Solar Geoengineering on Malaria Transmission in South Asia. Authorea Preprints.
Synopsis: This study examines the impact of Solar Geoengineering (SG) on malaria distribution in seven climate-vulnerable South Asian countries. Using Entomological Inoculation Rate (EIR) and Length of Transmission Season (LTS) as indicators, results from a dynamical malaria model show that the G6sulfur SG scenario leads to an overall decrease in malaria distribution from 2020 to 2090 compared to the SSP585 scenario. Significant declines in malaria are projected for Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan, while Afghanistan, Iran, and Nepal show moderate decreases in EIR, indicating a potential positive effect of SG on malaria transmission dynamics in these regions.
Effective control mechanisms of research on climate engineering techniques for the public good – the London Protocol regulatory approach as a role model
Ginzky, H., & Oschlies, A. Effective control mechanisms of research on climate engineering techniques for the public good–the London Protocol regulatory approach as a role model. Frontiers in Climate, 6, 1474993.
Synopsis: This study advocates for the governance of climate engineering techniques, emphasizing the London Protocol as a model for regulating emerging technologies like Carbon Dioxide Removal and Solar Radiation Modification. The authors argue that public funding and appropriate regulatory frameworks are crucial for overseeing in situ research and development. They suggest that the London Protocol’s framework for marine geoengineering could effectively inform governance schemes for other climate engineering approaches, ensuring responsible research and potential deployment.
A model study exploring the decision loop between unilateral stratospheric aerosol injection scenario design and Earth system simulations
Diao, C., Keys, P., Bell, C. M., Barnes, E. A., & Hurrell, J. W. (2024). A model study exploring the decision loop between unilateral stratospheric aerosol injection scenario design and Earth system simulations.
Synopsis: This paper develops a framework integrating unilateral SAI scenario design with geopolitical game theory and Earth system model simulations. Using the Community Earth System Model (CESM), a plausible unilateral SAI initiation scenario is simulated, revealing complex feedback loops between SAI deployment and subsequent climate impacts. The findings underscore the necessity of exploring unilateral SAI scenarios within the context of global cooperation and strategic decision-making.
Impacts of Solar Geoengineering on Projected Climate of South Asia
Hussain, A., Khan, M. A., & Sipra, H. (2024). Impacts of Solar Geoengineering on Projected Climate of South Asia. Authorea Preprints.
Synopsis: Solar geoengineering (SG), specifically stratospheric aerosol injection, is investigated for its potential impacts on temperature and precipitation patterns in climate-vulnerable South Asia. Under the SG G4 scenario, temperatures are projected to decrease by -0.62 °C, showing significant cooling effects during both the implementation phase (2020-2029) and continuation phase (2030-2069). While a cold bias is noted compared to RCP 4.5 projections, precipitation decreases slightly by -0.02 mm/day during the implementation phase, with no significant changes anticipated during the later phases.
Addressing the urgent need for direct climate cooling: Rationale and options
Baiman, R., Clarke, S., Elsworth, C., Field, L., MacCracken, M., Macdonald, J., ... & Tulip, R. (2024). Addressing the urgent need for direct climate cooling: rationale and options. Oxford Open Climate Change, 4(1), kgae014.
Synopsis: This study proposed an integrated approach to combat climate change by emphasizing several key strategies. First, it advocates for the research and deployment of large-scale cooling influences, particularly starting in polar regions, to address immediate temperature increases. In addition, the implementation of local and regional cooling measures that support adaptation efforts is recommended. The authors stress the importance of accelerating emissions reductions, especially targeting short-lived climate pollutants. Finally, they call for enhanced large-scale carbon removal initiatives to draw down legacy greenhouse gases.
Pushing Radiative Cooling Technology to Real Applications
Lin, C., Li, K., Li, M., Dopphoopha, B., Zheng, J., Wang, J., ... & Huang, B. (2024). Pushing Radiative Cooling Technology to Real Applications. Advanced Materials, 2409738.
Synopsis: Radiative cooling technology presents a viable strategy for combating global warming while promoting energy efficiency. Despite progress, five critical challenges hinder its practical application: improving optical efficiency, preserving aesthetic appeal, controlling overcooling effects, enhancing durability, and scaling up manufacturing processes. This review outlines the optical principles of radiative cooling and addresses these challenges, proposing advanced solutions through innovative structural designs, material choices, and fabrication methods, ultimately guiding future research and industry efforts in this field.
Drivers and attitudes of public support for technological solutions to climate change in 30 countries
Brutschin, E., Baum, C. M., Fritz, L., Low, S., Sovacool, B. K., & Riahi, K. (2024). Drivers and attitudes of public support for technological solutions to climate change in 30 countries. Environmental Research Letters, 19(11), 114098.
Synopsis: Public attitudes toward CDR and SRM technologies vary significantly across different countries. Surveys in 30 nations reveal that skepticism is most pronounced in wealthier countries, where trust in science and technology is lower, and personal climate change impacts are perceived as less severe. Conversely, many middle-income countries show higher support for CDR and SRM, despite potentially lacking the capacity for effective implementation. This highlights the need for tailored climate strategies that consider local contexts and emphasize international collaboration and governance to responsibly manage these technologies.
Impact of Solar Radiation Management on Andean glacier-wide surface mass balance
Fernández, A., Manquehual-Cheuque, F., & Somos-Valenzuela, M. (2024). Impact of Solar Radiation Management on Andean glacier-wide surface mass balance. npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, 7(1), 257.
Synopsis: The impact of SRM on the surface mass balance of Andean glaciers examined in this paper reveals a consistent negative mass balance across all climate scenarios analyzed for the 21st century. However, SRM does influence interannual variability and temperature sensitivity in certain regions. Had SRM been adopted in the late 1980s, it could have significantly altered the current negative trends. Given the diverse hydroclimatic regimes present in the Andes, these results underscore the critical need for urgent emissions reductions to preserve these vital ecosystems.
An open letter to the IMO supporting maritime transport that cools the atmosphere while preserving air quality benefits
Baiman, R., Bishop, R., Elsworth, C., Gadian, A., Melton, B., Petersen, O., & Tao, Y. (2024). An open letter to the IMO supporting maritime transport that cools the atmosphere while preserving air quality benefits. Oxford Open Climate Change, 4(1), kgae008.
Synopsis: This open letter highlights a global warming emergency worsened by the decline in anthropogenic atmospheric aerosol levels, particularly due to International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations on bunker-fuel sulfur oxides. The letter suggests reconsidering these regulations by temporarily relaxing sulfur emissions for "high seas" shipping to enhance cooling benefits while preserving air quality in coastal areas. It advocates for research into benign aerosol alternatives, such as Marine Cloud Brightening and Tropospheric Aerosol Injection, to replace the cooling effects of sulfur emissions without harming humans or ecosystems.
WEB POSTS
How solar geoengineering could disrupt wind and solar power (Carbon Brief)
Solar radiation modification: NOAA State of the Science factsheet (Climate.gov)
Accelerating climate intervention research to improve climate security (Atlantic Council)
Stratospheric Plan (Dawn Aerospace)
Solar geoengineering research could get funding injection (Global Enterprise)
Non-intrusive geoengineering and other emerging energy applications enabled by ultralight 4G planar optics (SPIE)
Geoengineering Can Save the Planet — If We Demystify It (Bloomberg)
Scientists have said that we can cool the planet back down. Now they’re not sure it will be so easy (The Washington Post)
Breaking Down Barriers at Climate Week NYC (DSG)
Arctic Futures: White Shield or Blue Economy—Multiplying proposals for ice restoration face geopolitical obstacles (Legal Planet)
Scoping Note on Applicable Legal Frameworks for SRM (Co-Create Project)
So You Want to Geo-Engineer the Earth (Jacob Rintamaki)
We know how to cool the planet. Is it worth the risk? (The Times)
The moral hazard argument against geoengineering makes no sense (One Percent Brighter)
Startup Make Sunsets Wants to Fight Global Warming by Making Aerosol Clouds (Inc)
Buying time: can science save the Great Barrier Reef? (University of Cambridge)
ECLAC’s new background paper on SRM: an important tool for climate policy in Latin America and the Caribbean (SDG)
The Imperative for Marine Cloud Brightening: A Call for $100 Million to Preserve Arctic Sea Ice (Climate Genn)
Milton: Termination Shock Now (One Percent Brighter)
Geoengineering: Building ethics, transparency and inclusion into climate intervention research (World Economic Forum)
Geoengineering gets guidelines after high-profile blunders (E&E NEWS)
An Ethical Framework for Climate Intervention Research—Can the AGU’s new principles defuse controversy and enable responsible research? (Legal Planet)
Stormfury—Paint the roofs white (a geoengineering taxonomy) (Keepcool)
REPORTS
Accelerating Climate Intervention Research to Improve Climate Security (SilverLining)
Ethical Framework Principles for Climate Intervention Research (AGU)
Addressing Solar Geoengineering within the CBD Framework (SDG)
JOB OPPORTUNITIES
Post-Doc Reserchers Position—The Climate Sytems Engineering Initiative at University of Chicago | Deadline to apply: 15 November 2024
"The University of Chicago is building a substantial research cluster (including an anticipated ten new faculty lines) on the science, technology, and public policy of Climate Systems Engineering. Our goal is to advance understanding of the benefits, risks, and governance of technologies that might reduce the impacts of accumulated greenhouse gases, and to educate students who will face the challenges of managing industrial civilization on a fragile planet. CSEi’s topical scope includes open-system carbon removal such as enhanced weathering, solar geoengineering, and interventions to limit loss of glacial ice. CSEi welcomes research from across fields including the sciences, humanities, social sciences, public policy, and law.
The CSEi Postdoctoral Researchers program aims to develop the next generation of research leaders who will shape the future of climate systems engineering for the benefit of people and the planet. CSEi Postdoctoral Researchers will work closely with UChicago faculty mentors, but their research and funding are independent, and the program will help them develop strong research networks by facilitating collaboration among the postdoctoral cohort and by ensuring that they have ample opportunities to interact with the full community of CSEi-affiliated faculty and research leaders. Securing a faculty mentor in advance is strongly preferred, and applicants are encouraged to reach out early to engage a mentor. UChicago faculty members from any discipline may potentially serve as a mentor, regardless of whether they have prior experience with climate systems engineering."
Communications Specialist at the University of Chicago | Chicago
"The University of Chicago is building a substantial research cluster (including an anticipated ten new faculty lines) on the science, technology, and policy of climate systems engineering. The goal of the Climate Systems Engineering initiative (CSEi) is to advance understanding of the benefits, risks, and governance of technologies that might reduce the impacts of accumulated greenhouse gases, and to educate students who will face the challenges of managing industrial civilization on a fragile planet. CSEi’s topical scope includes open-system carbon removal such as enhanced weathering, solar geoengineering, and interventions to limit loss of glacial ice; and we welcome research from across fields including the sciences, humanities, social sciences, public policy, and law."
Postdoctoral researcher on climate modelling of aerosol-cloud interactions at ETH Zürich | Zürich, Schweiz
"The Atmospheric Physics Group of Prof. Ulrike Lohmann at the Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Sciences at ETH Zurich (IAC-ETH) invites applications for a 2-year Postdoc position within the project "Glaciogenic seeding on mixed-phase clouds for radiation management (GLANCE)", funded by the Solar Radiation Management (SRM) programme of the Simons Foundation."
Funded PhD Positions in Multiscale Modeling of Stratosphere and Aerosol-Cloud Interactions at the University of Hawaii at Manoa
"Hongwei Sun Group focuses on developing and applying various modeling methods to study multiscale atmospheric processes, including (1) large-scale stratospheric transport, dynamics, and aerosols and (2) small-scale aerosol-cloud interactions. Students can also study applications of (1) and (2) in climate engineering (or geoengineering) if interested."
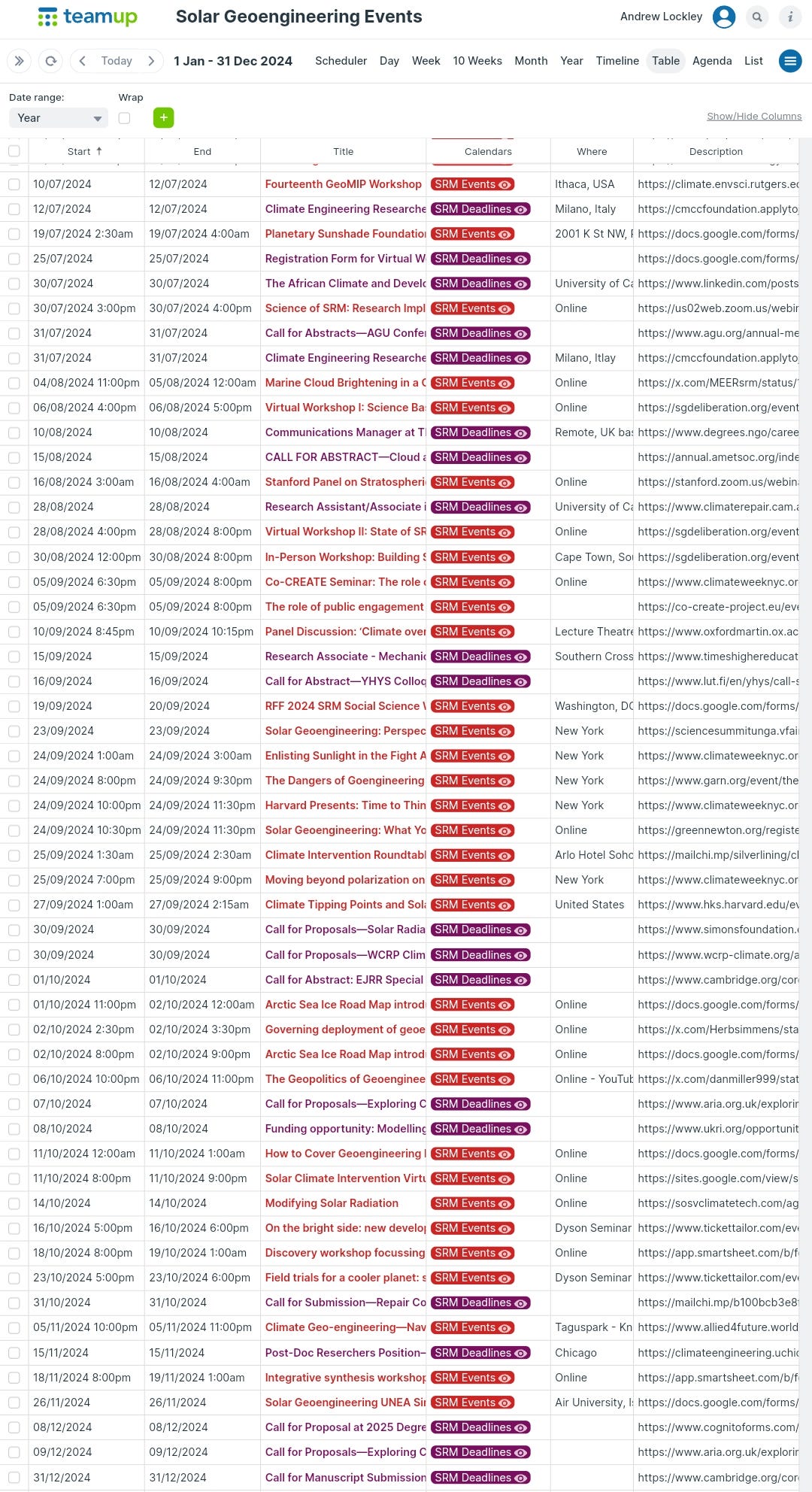
UPCOMING EVENTS
(NEW) Climate Geo-engineering—Navigating the Landscape of Climate Change Solutions at World Future Forum by Allied4Future | 05 November 2024 | Oeiras (In-person & Online)
Climate Repair Seminar Series - Autumn 2024
Ethics and Governance (title TBA) | 06 November 2024
Good COP, Bad COP: a post-COP29 assessment | 27 November 2024
(NEW) Solar Radiation Modification: A Conversation on Governance and Research at COP29 by The Degrees Initiative | 11 November | Baku, Azerbaijan
(NEW) Solar Climate Intervention Virtual Symposia # 14 | 15 November 2024 | Online
Integrative synthesis workshop focusing on identifying gaps in current governance & ethics | 18 November 2024 | Online
(NEW) Solar Geoengineering UNEA Simulation by FASS at Air University & DSG | 26 November 2024 | Islamabad, Pakistan
(NEW) SRM Discussion: A Measured Analysis on a Potential Avenue for Combatting Climate Change by Duke Law School | 04 December 2024 | North Carolina
2025 Solar Radiation Management Annual Meeting by Simons Foundation | 24-25 April 2025 | New York
The 2025 Degrees Global Forum | 12-16 May 2025 | Cape Town, South Africa
Artic Repair Conference 2025 by University of Cambridge & Center for Climate Repair | 26-28 June 2025 | Cambridge UK
GUIDELINES:
Sync selected events to your default calendar in these simple steps:
1) Click on the event you want to sync.
2) Tap the menu icon (three vertical lines) at the top left.
3) Choose 'Share.'
4) Pick your default calendar.
5) Save the event.
Sync the entire Teamup Calendar to your default calendar with these simple steps:
1) Tap the menu icon (three vertical lines) at the top right.
2) Choose 'Preferences.'
3) Click 'iCalendar Feeds.'
4) Copy the URL shown for 'Solar Geoengineering Events / SRM Deadlines.'’
5) Paste the URL into your default calendar settings (Open Google Calendar in your web browser if you are using Gcal).
6) Click 'Subscribe' or 'Add Calendar.'
For more detailed instructions, visit: https://calendar.teamup.com/kb/subscribe-to-teamup-icalendar-feeds/
You can directly sync all Solar Geoengineering events to your default calendars by pressing the link below:
PODCASTS
Is cirrus thinning dead? Jeggle | Reviewer 2 does Geoengineering
"Kai Jeggle explains to @geoengineering1 how off-target effects of cirrus cloud thinning mean that it can never be used effectively. Paper; Jeggle, K., Neubauer, D., Binder, H., and Lohmann, U.: Cirrus formation regimes – Data driven identification and quantification of mineral dust effect, EGUsphere [preprint], https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2024-2559, 2024."
Solar Radiation Management's Risks and Opportunities | Climate on the Edge
"In this episode I explore the controversial topic of solar geoengineering with Dr. Holly Jean Buck, and Dr. Will Burns, two of the most thorough and interesting thinkers out there when it comes to the topic. Specifically they talk me through the question of “should we ban SRM research”.
There’s a lot these two experts disagree on about SRM, and their back and forth really expanded my thinking on the topic. Together, we break down what SRM is, how it might work, and the different approaches within SRM, such as stratospheric aerosol injection and marine cloud brightening.
This episode provides a nuanced look at SRM as part of the climate action toolkit, I hope it helps you think critically about the role it might play, as it did for me.”
SRM ethics - Hofbauer | Reviewer 2 Does Geoengineering
"Benjamin Hofbauer discusses 3 papers from his PhD, on the ethics of Solar geoengineering. Hofbauer, B. (2023). Systemic risks and solar climate engineering research. Integrating technology ethics into the governance of systemic risks. Journal of Risk Research, 26(12), 1383–1395. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2023.2288010
Hofbauer, B. (2023). Normative Uncertainty in Solar Climate Engineering Research Governance. Ethics, Policy & Environment, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/21550085.2023.2216148
Benjamin Hofbauer. Techno-moral change through solar geoengineering: How geoengineering challenges sustainability. Prometheus. 2022. Vol. 38(1). DOI: 10.13169/prometheus.38.1.0082"
Solar Radiation Management to Buy Time for Climate | Climate on the Edge
"As a climate investor focused on energy transition and carbon dioxide removal, I've spent years understanding and supporting technologies that drive decarbonization. But lately I've grown concerned that our progress isn't happening fast enough. The urgency of our situation. Which has become very apparent has left me curious about what else is out there.
That's why I was so excited to speak with Kelly Wanser, Executive Director of SilverLining. SilverLining is a nonprofit organization dedicated to addressing climate risks through advancing research and equitable governance around solar radiation management. Kelly is an absolute powerhouse here and a true pioneer in this field. Our conversation will get into how SRM might work, where it's at today, what's needed to advance the field and why organizations like SilverLining and its backers believe that it should advance.
We'll explore the economic and practical aspects, including concerns about SRM's affordability and the actual, very real logistical challenges of deploying any form of SRM responsibly on a global scale. Kelly is one of the world's most influential figures on SRM and climate intervention beyond emissions reduction. I hope this conversation is as thought-provoking for you as it was for me."
Silicon Valley Elites Want to Block the Sun. Not Everyone’s On Board | Big Take
"It sounds like science fiction, but it’s real: Venture capitalists, startup founders, and Silicon Valley elites are pouring money into a controversial technology called solar radiation modification that could cool the planet by blocking the sun.
Today on the show, host Sarah Holder talks to Bloomberg reporter Sophie Alexander about the international coordination needed for something like this to work, and why funding for it is ramping up even as researchers express concerns about the possible consequences."
YOUTUBE VIDEOS
Has the Atlantic AMOC system ALREADY started to collapse?? | Just Have a Think
"AMOC, or The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, has collapsed many times in Earth's geological history. But it's never happened while modern civilisations have existed - at least not until now anyway. We're already struggling to cope with 0.2 degrees Celsius of warming each decade, but an AMOC collapse could bring such catastrophic seasonal disruption that it would make recent extreme weather events look like a walk in the park! So, what's the plan??"
Harvard @ Climate Week NYC | Time to Think About Solar Geoengineering? | The Salata Institute at Harvard University
"A thought-provoking discussion on the emerging and controversial topic of solar geoengineering. This event brought together renowned experts to explore the broader context of climate change and the rising interest in solar geoengineering.
Topics Covered:
-What are the scientific and engineering challenges of solar geoengineering?
-How should we think about the ethical and cultural dimensions of solar geoengineering? Why does this technological approach seem frightening to many experts?
-Why is solar geoengineering receiving more attention in recent years? Does it imply that the decarbonization is failing?
-What are the geopolitical challenges of solar geoengineering? Will this interfere with the international climate agreements?
-How should universities engage with solar geoengineering? What are the research challenges for the next decade?"
The Geopolitics of Geoengineering with Cynthia Scharf | Climate Chat
"In this Climate Chat episode, we will discuss the need for governance of both research and deployment of solar geoengineering, aka, Solar Radiation Management (SRM) with Cynthia Scharf who is senior advisor to the International Center for Future Generations, a European think tank, where she leads their work on climate intervention technologies."
Operaatio Arktis: Interview with Clara Botto, 2024 | Operaatio Arktis
"Clara has been engaged with sustainable development at a grassroots and international level, from arts to politics, for the past 9 years. Clara works in Just Deliberation on Solar Geoengineering (DSG) and for the period 2024-2025 she is also working as a fellow with the Communications team of the UNFCCC and UNU-EHS. Above all that Clara Botto is our friend and dear colleague who wants to save the world as much as we want.
We discussed fears and concerns about Solar Radiation Modification research. Who needs to be discussing these things on the decision making tables? Are we there yet? Let’s find out."
Varisha Khan: Interview with SRM Youth Watch | SRM Youth Watch
"Varisha Khan is an MSc student of Health Informatics working as a Research Associate under a project at COMSATS University, Islamabad. The institute has a leading team devoted to climate action in the context of geoengineering, focusing on the Global South. Varisha’s goal is to scrutinise the “Trade-off Based Impacts of SRM on Malaria Distribution across South Asia, particularly Pakistan"."
DIY Geoengineering @ Hope XV | Luke Iseman
DSG's intervention at the UN High-Level Plenary Meeting on Sea Level Rise | DSG
“DSG's Director of International Policy Alia Hassan spoke at the UN General Assembly High-level plenary meeting on addressing existential threats posed by sea level rise."
Solar Climate Intervention Virtual Symposium 13 (Prof. Govindasamy Bala & Dr. Kelsey Roberts) | Solar Climate Intervention Talks
"Solar Climate Intervention Virtual Symposium 13
Prof. Govindasamy Bala (Indian Institute of Science, India) : "Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering and Tropical Monsoon Rainfall"
Dr. Kelsey Roberts (Louisiana State University, USA) : "Towards Estimating Marine Ecosystem Impacts of Climate Intervention"
Solar Geoengineering: Promise or Peril for Climate Change? | Edu now.
"In this episode, we dive into the controversial world of solar radiation modification (SRM), also known as solar geoengineering, as a potential tool to combat climate change. Drawing on insights from Janos Pasztor's article, we explore the science behind SRM and its potential to cool the planet. But with great power comes great responsibility—SRM raises critical ethical, environmental, and governance challenges. Could unchecked use of this technology worsen global inequalities or destabilize international relations? Join us as we discuss the urgent need for international collaboration and open dialogue to responsibly navigate the future of solar geoengineering."
SPF 1000: Modifying Solar Radiation SOSV CLIMATE TECH SUMMIT 2024 | SOSV
"Given that global temperatures have hit record highs 13 months in a row, it’s reasonable to ask whether decarbonization can move fast enough. What if extreme weather events produce huge death tolls? One response could be to pump sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere to cool the planet by reflecting the sun’s energy away from earth. Controversial in the extreme, yes, but more than ever the object of well-funded research. Our panel looks at the state of the debate over this extreme climate tech. The speakers are David Keith (University of Chicago) Ryan Orbuch (Lowercarbon Capital) and Janos Pasztor (independent consultant.).The moderator is Cat Clifford, who is a correspondent at Cipher."
How to Cover Geoengineering | Mongabay Webinars | Mongabay
"As the climate crisis worsens, scientists and policymakers are increasingly considering geoengineering concepts as a potential solution. However, deploying or researching technology, like solar geoengineering, remains highly controversial, with scientists on either end of the divide.
In this Mongabay webinar, journalists will learn how to better cover solar geoengineering, while exploring the policy, research, and ethical questions surrounding it."
Pasztor, Parson and Baiman Healthy Planet Action Coalition | Healthy Planet Action Coalition
"Dr Ted Parson, Professor of Environmental Law and Faculty Director of the Emmett Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has led and served on multiple advisory committees for the National Academy of Sciences, the U.S. Global Change Research Program, and other national and international bodies. His work was influential in establishing the World Commission on Climate Overshoot, for which he serves as a senior advisor. He was formerly Joseph L. Sax Collegiate Professor of Law and Professor of Natural Resources and Environment at the University of Michigan, and spent twelve years on the faculty of Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government.
Mr Janos Pasztor was most recently Executive Director of the Carnegie Climate Governance Initiative (C2G). Before that he served as UN Assistant Secretary-General for Climate Change, and Senior Advisor to the UN Secretary-General. Earlier, he held various positions inter alia at the secretariat of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and WWF International. He holds a B.Sc. and M.Sc. in Nuclear Engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
Dr. Ron Baiman is an HPAC Co-Founder and member of the Steering Circle and a retired professor of Economics long time "radical" or progressive economist."
Solar Geoengineering: Benefits & Risks with Daniele Visioni | Climate Chat
"In this Climate Chat episode, we will discuss the benefits and risks of cooling the Earth by implementing solar geoengineering (a.k.a, Solar Radiation Management or Sunlight Reflection Methods - SRM) with Cornell climate scientist Daniele Visioni."
Solar Geoengineering Research Program Lunch Talk with Daniele Visioni | The Salata Institute at Harvard University
"Daniele Visioni obtained his Ph.D. in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics from the University of L’Aquila, in Italy, in 2018. He moved to Cornell in the same year, where he started as a Postdoctoral Associate in the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. In 2022, he continued on as a Research Associate in the same department, and also became a Research Scientist I at the National Center for Atmospheric Science (NCAR). He joined EAS in the fall of 2023 as Assistant Professor, and retains a courtesy appointment as Affiliate Scientist at NCAR in the Atmospheric Chemistry, Observation and Modeling (ACOM) lab. He’s the co-chair of the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP), and has been a coauthor of the Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2022."
LIVE SHOW - Solar Geoengineering: Should we go there? - Part II | Energy vs Climate
"David and Ed hit the stage at the Energy Disruptors: UNITE 2024 summit in Calgary to discuss solar geoengineering, a major focus of David's academic research. Together, they unpack the technical and non-technical dimensions of solar geoengineering, including global governance and decision making."
Arctic Modeling Research on Stratospheric Aerosol Injection and Solar Radiation Modification | IARPC Collaborations
"This meeting of the Modelers Community of Practice focused on the federal government's role in research into solar radiation modification (SRM), a potential means to mask the effects of global warming. We explored the intersection of Earth system modeling, SRM research, and the Arctic Research Plan, and looked at modeling results.
Gregory Frost and Victoria Breeze (NOAA) presented on NOAA's Earth Radiation Budget Program. Ewa Bednarz (CIRES/NOAA) presented "Stratospheric Aerosol Injection: Modeling the Impacts on Atmospheric Radiation, Dynamics and Chemistry."